Diodes are two-terminal and nonlinear circuit elements which only allow current to flow in one direction, implemented using p-n junctions.
Current/Voltage Models
Ideal Model
Open circuit when , and shorted when .

Constant Voltage Model
Only passes current when . Typically for silicon diodes.
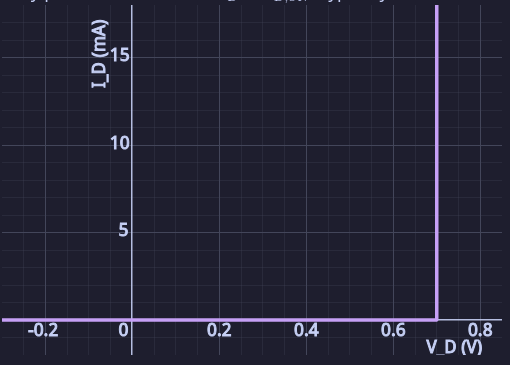
Non-Ideal Exponential Model
Shockley Diode Equation
reverse-bias saturation current
thermal voltage ( at )
Can also be modelled with linear piecewise function.

Solving for current and voltage
Solve iteratively
Small Signal Model
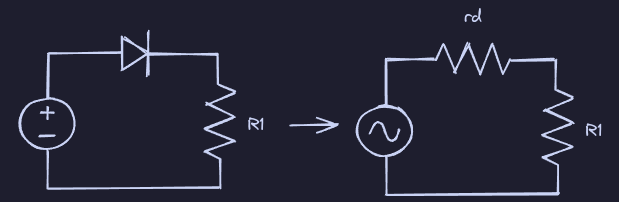
Uses
Rectifier
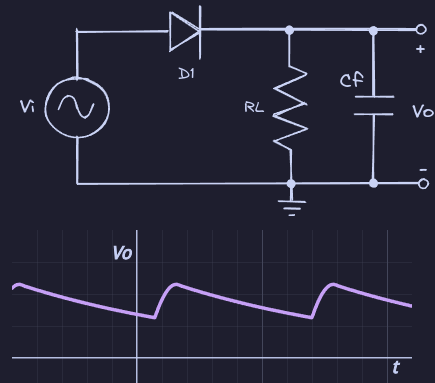
Rectifiers convert AC to DC by using a diode to only allow half of an AC source’s voltages. A capacitor may be used for filtering out AC frequencies and to act as a reservoir.
Half Wave Without Capacitor

Half Wave With Capacitor
Full Wave Without Capacitor
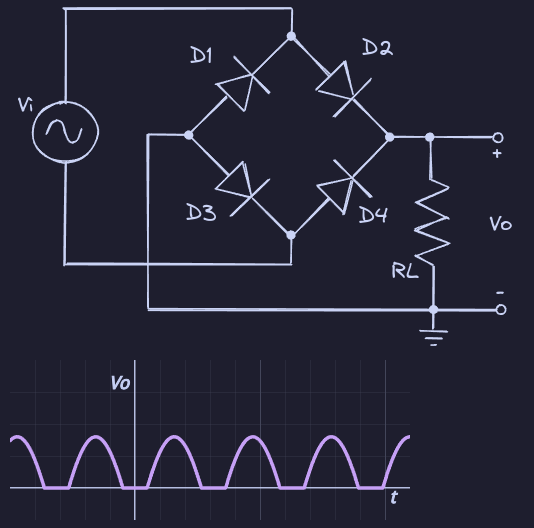
Full Wave With Capacitor

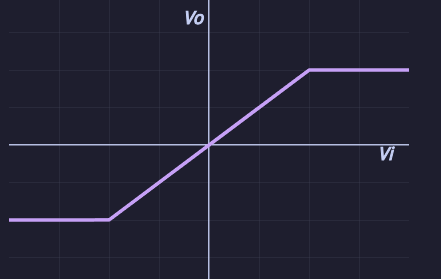
Voltage Limiter
Clips voltages which exceed certain thresholds.
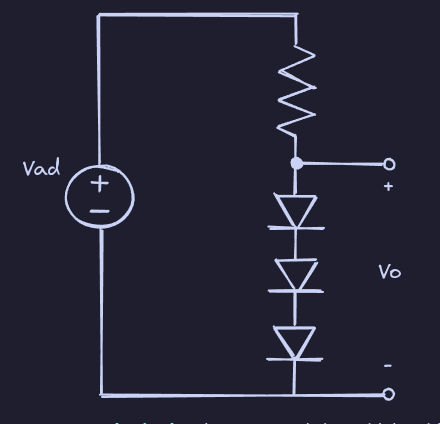
Voltage Regulator
A voltage regulator generates constant DC voltage. A simple voltage regulator uses many diodes in series, while a more common implementation involves using a zener diode in breakdown.
Power-supply ripple: The unwanted sinusoidal residue in a regulator.
DC Power Supply
Power transformer reduces 120V voltage to 8-12V
Diode rectifier converts bipolar voltage to unipolar
Filter reduces voltage variations
Voltage regulator further reduces voltage and ripple